Approximately 75% of oral cancers are attributed to the use of tobacco with chronic alcohol consumption as another leading risk factor. The combined use of tobacco and alcohol will increase this risk further.
Although oral cancer accounts for two to four percent of all cancers diagnosed annually, the 5-year survival rates are among the lowest. Although risks increase with age, the survival rate of cancer patients between the ages of 18-39 is lower than that of cancer patients above the age of 40.
The 5-year survival rate for oral cancers highly depends on the stage at which it is discovered:
- Stage I 90% survival
- Stage II 65% survival
- Stage III 40% survival
- Stage IV 10% survival
Unfortunately, 70% of oral cancers are diagnosed in stages III and IV, the late stages. For those among us who actually survive late stage detection, a more disfiguring outcome is inevitable, including difficulty eating, drinking, and speaking.
While our lifestyles dictate our increased risk, we are all at risk. 25% of oral cancers occur in people who don’t smoke and have no other risk factors. Signs and symptoms of oral cancer include one or more of the following:
- Mouth sores that fail to heal or bleed easily
- White or red patches in the mouth that are chronic and persistent
- Lump, thickening or soreness in the mouth, throat, or tongue
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing food
The key to fighting oral cancer is early detection, but identifying lesions early is difficult with an unaided visual examination. To provide oral cancer screening and detection we recommend you have a VelScope® exam.
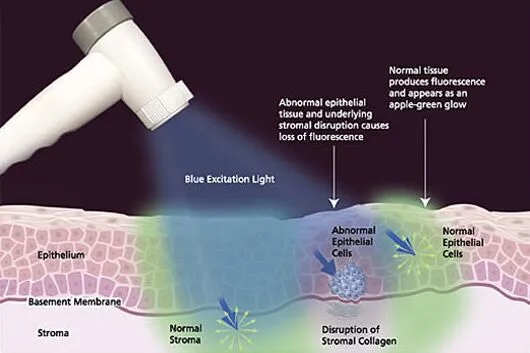
The VelScope® exam involves using a special Handpiece that emits a safe blue light into the oral cavity, causing tissue fluorescence from the surface of the epithelium through to the basement membrane, where pre-malignant changes typically start and in the stroma beneath. The special, patented optical filtering in the Handpiece allows the clinician to immediately view the different fluorescence signatures from the oral tissue to help differentiate between normal and abnormal tissue.
Abnormal tissue, such as dysplasia or cancerous lesions, typically appear as irregular, dark areas that stand out against the otherwise normal, green fluorescence pattern of surrounding healthy tissue. This technology thus helps dental practitioners identify potentially dangerous growths that might have been missed with the naked eye, yet this exam takes only 2-to-3 minutes. Oral cancer screening and detection is the key to fighting oral cancer!
